We need to get the campaign to eradicate polio back on track
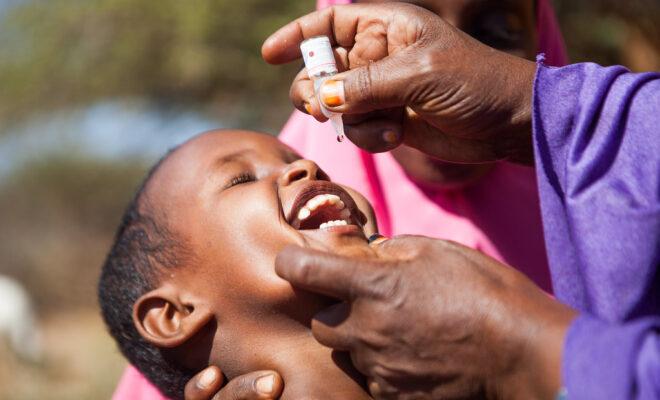
A recent case of polio in Malawi has sparked an intensive immunisation campaign in the region.
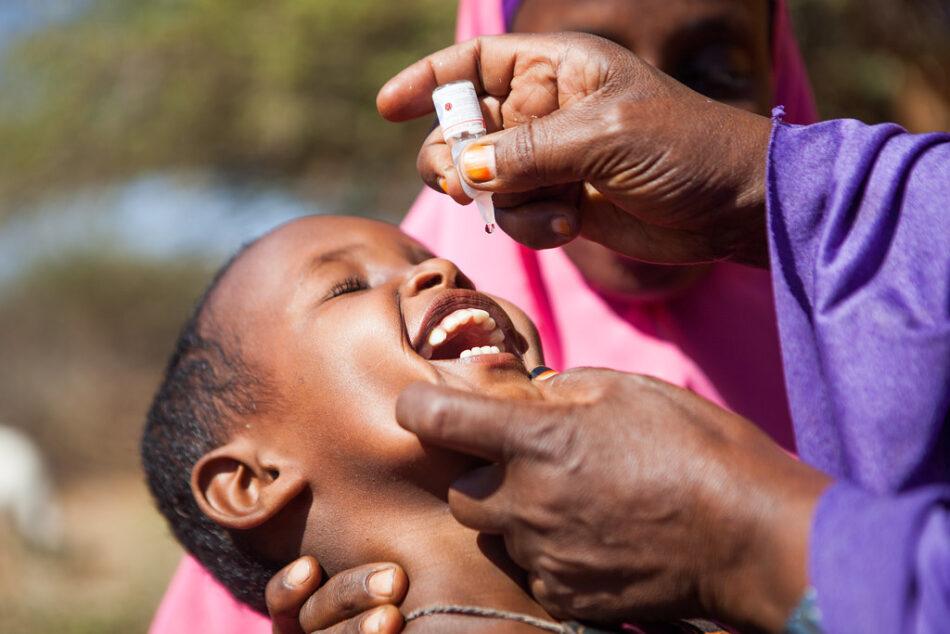
Polio vaccinations are administered in Ethiopia following an outbreak. Credit: UNICEF Ethiopia/2013/Sewunet.
In the outskirts of Malawi’s capital, Lilongwe, just beyond where paved roads transition to dirt, an undiagnosed polio infection paralysed a three-year-old girl this February. From one day to the next, the child’s life was changed forever.
Among Africa’s public health community, we had looked at our successes against wild poliovirus as a cause for optimism. In the 1990s, the disease paralysed more than 75,000 African children every year. But following extensive immunisation campaigns coupled with strong surveillance, the wild poliovirus was officially kicked out of sub-Saharan Africa just under two years ago. We went from 300,000 cases in 1985 to zero in 2020, just as the Covid-19 pandemic struck. In Malawi, there had been no case of wild poliovirus since 1992, and for many, the disease had become a distant memory.
Polio is a viral infection that causes nerve damage and, in some cases, paralysis that can lead to permanent disability or even death. It is transmitted mostly through contaminated water or food, and its symptoms – fever, sore throat, headaches, pain in the arms and legs – are so generic that an active infection is often difficult to diagnose until paralysis strikes.
While polio remains endemic to Afghanistan and Pakistan, with a few dozen cases identified every year in each country, it has been eradicated just about everywhere else. The Americas were declared polio-free in 1994; China, Australia, and the Western Pacific countries in 2000; Europe in 2002; and Southeast Asia in 2011. The last cases in Africa were in Nigeria, in 2016, in the north of the country where the horrors of armed conflict had upended immunisation efforts.
But over the past two years, the Covid-19 pandemic has disrupted efforts to combat vaccine-preventable diseases, including polio, in many other places. The four-month suspension of polio vaccination campaigns in more than 30 countries in 2020, coupled with related disruptions to essential immunisation services, led to tens of millions of children missing polio vaccines. Including the three-year old girl in Malawi who is now paralysed for life.
We know a lot about wild poliovirus now, enough to trace the case in Malawi to a strain of the virus originating in Pakistan. While this new detection does not affect the African region’s wild poliovirus-free certification status, it has set the world back in its efforts to eradicate the disease. And if transmission is not stopped within the next 12 months, the continent’s certification status would likely be revisited. This disease creates far too much devastation, on a personal and health system level, for us to allow that to happen.
We can detect the presence of the virus, along with its genetic origins, through sampling urban sewers – and so we have launched surveillance efforts in Lilongwe and cities in neighbouring countries. We’ve also deployed healthcare workers to go door-to-door in Malawi, identifying families whose children have unexplained paralysis, and securing samples for testing to see if polio was the cause.
With support from international and local partners, governments in the region have now launched an intensive immunisation campaign, with the intent of vaccinating more than 23 million children in Malawi and its neighbours Tanzania, Zambia and Mozambique, as well as Zimbabwe. The vaccine needs to be administered in multiple doses, so the logistics of reaching out to both urban and rural locations, with trained staff who carry sufficient numbers of doses, has to be well planned and executed. Luckily, we are benefiting from lessons learned from experiences in Syria and Somalia in recent years, where the polio programme quickly stopped the spread of imported wild poliovirus, despite challenges posed by on-going conflict and insecurity.
It was no coincidence that the African Region achieved its wild polio-free status two years ago. This only happened because of the decades of commitment by governments, communities and partners, and we are now leveraging the wealth of experience and expertise we have built in the region to move quickly to bring this outbreak under control.
The payoff is immense. Globally, eradication efforts have saved the lives of an estimated 180,000 people and spared an estimated 1.8 million children from disability. The economic benefit for ending polio have been projected at upwards of $50 billion by 2035, with the vast majority of these benefits accruing to low-income countries freed from having to handle such a terrible health threat.
Eliminating polio is about more than an economic stimulus, of course. We do it because it is a source of suffering that we can remove from this world, because every child paralysed by a polio infection is one child too many. Wild poliovirus cases around the world are at an all-time low, and we have a historic opportunity to stop the transmission of the virus for good. To achieve this, we need governments throughout Africa – especially the southern nations – to join these efforts, step up surveillance, vaccinate their children, and get back on track to wipe this virus off the planet.






